Introduction
CLS (Classical Least Square) quantitation, which is one of the multivariate analyses, calculates quantitatively by using entire spectral data which varies depending on concentration. Therefore, it is an effective tool in the case that it is difficult to find a single peak for quantitation because of overlaid spectra of multicomponent. In addition, it also can perform the simultaneous quantitation of multicomponent. The advantages of CLS quantitation is as below.
- High accuracy by noise averaging from calculation using all spectral data in the specified spectral range
- Calculation of virtual component spectra by least squares method helps to analyze each information (spectrum) in multicomponent.
- Simultaneous monitoring of multicomponent by using automatic quantitation program
This article shows the evaluation example by using CLS quantitation method.

Versatile FTIR spectrometer with gas cell
Evaluation example
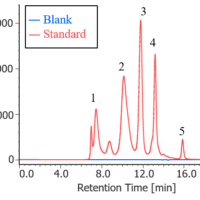
Figure 1 shows measurement result of each standard gas (100 ppm) by gas cell. Since absorption spectra of gases of CO, CO2 and N2O were overlapped, it is very hard to evaluate each concentration in multicomponent gas with high accuracy.
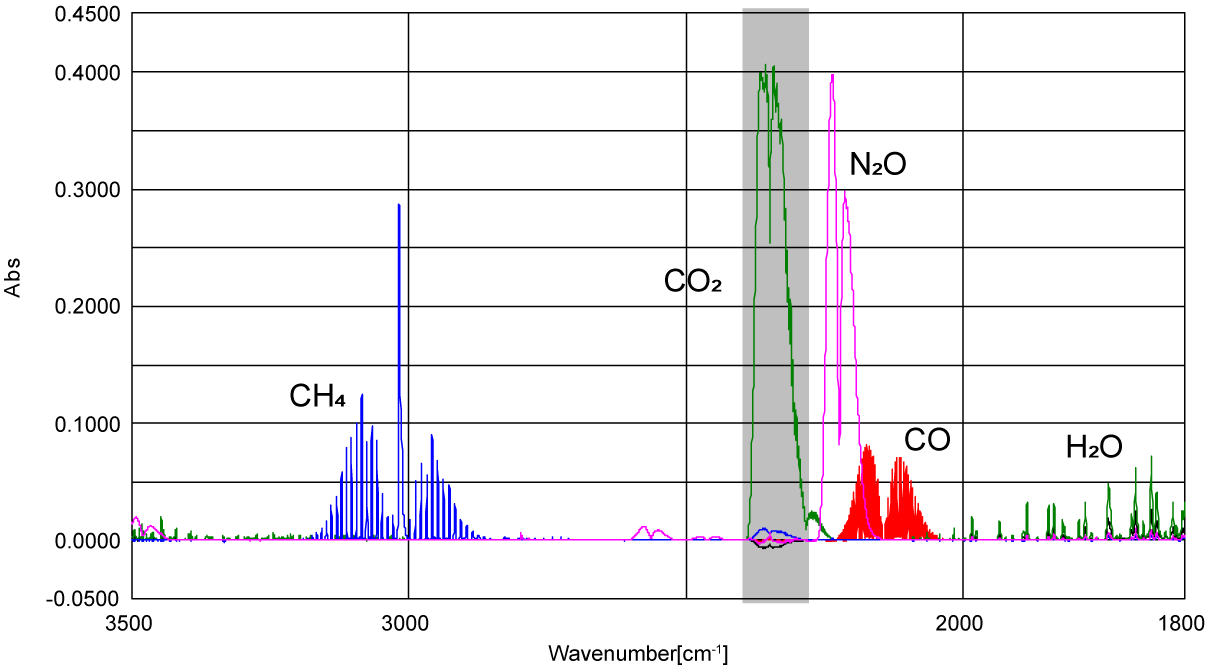
Figure 1. IR spectra of standard gases
Figure 2 show the CLS calibration models (CH4 and CO gas) measured by gas cell. The curves indicates good linearity in the range of 1-120 ppm, and the correlation coefficient was more than 0.98. The calibration models of CO2, N2O and H2O gas have been also created even if Figure is not shown.
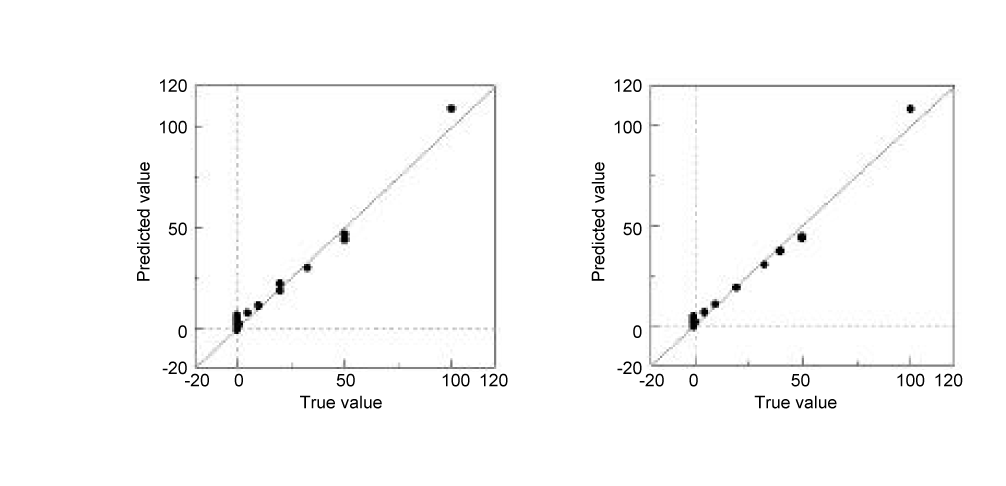
Figure 4. Calibration model (left: CH4, right: CO)