Introduction
There is increasing concern about aldehydes; such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde as environmental pollutants, which are contaminating the environment in the atmosphere, lakes and marshes, reservoirs, and rivers. Therefore, aldehydes are monitored under various regulations including, the Air Pollution Control Law, Water Supply Law, and Offensive Odor Control Law. As a method to measure aldehydes in the atmosphere using HPLC, the general method employed is to collect aldehydes in the atmosphere using a sampler enclosing silicagel containing 2,4- DNPH and extracting aldehydes derivatized after collection with acetonitrile. JASCO has developed a method for the analysis of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde using a post column fluorescence derivatization with 1,3- cyclohexanedione as the labeling reagent.
This method is used to analyze aldehydes in the atmosphere. As a result, aldehydes in the atmosphere extracted with water were analyzed successfully as well as the source of aldehydes in water.

LC-4000 HPLC system
Experimental
Experimental Condition
Column: Shodex RSpak KC-811 6E (6.0 mmID x 250 mmL)
Eluent: 3 mM Perchloric acid
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Reagent: 1,3-Cyclohexanedione in ammonium acetate buffer
Reagent flow rate: 0.4 mL/min
Column temp.: 60ºC
Reaction temp.: 120ºC
Wavelength: Ex. 366 nm, Em. 440 nm, Gain x10
Injection volume: 50 µL
Standard sample: Formaldehyde 0.1 mg/mL
In figure 1, the 1,3-cyclohexanedione reaction during the post column derivatization method is shown and figure 2 illustrates system flow diagram.
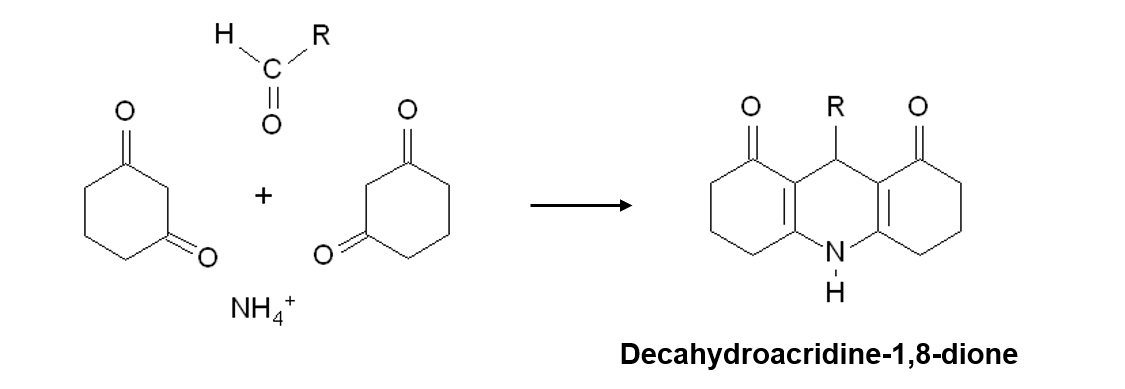
Figure 1. 1,3-Cyclohexanedione reaction during the post column derivatization method
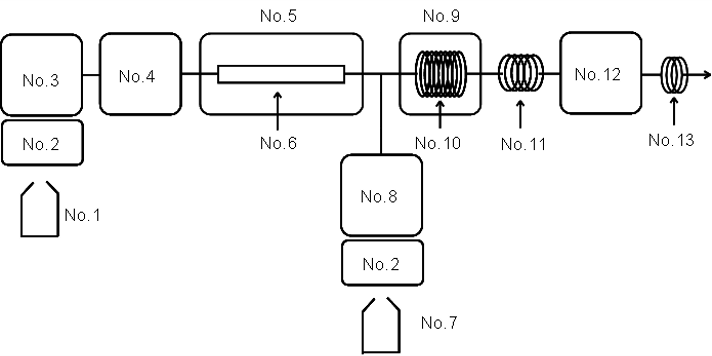
Figure 2. Flow system diagram
No.1 : Eluent, No.2 : Degasser, No.3 : Pump for eluent, No.4 : Autosampler, No.5 : Column oven, No.6 : Column (Shodex RSpak KC-811 6E), No.7 : Reagent, No.8 : Pump for reagent, No.9 : Reaction oven, No.10: Reaction coil, No.11: Cooling coil, No.12: Fluorescence detector, No.13: Backpressure coil
Figure 3 explains the usage of a passive gas tube for collecting the sample in the atmosphere and figure 4 shows the extraction method from the passive gas tube.
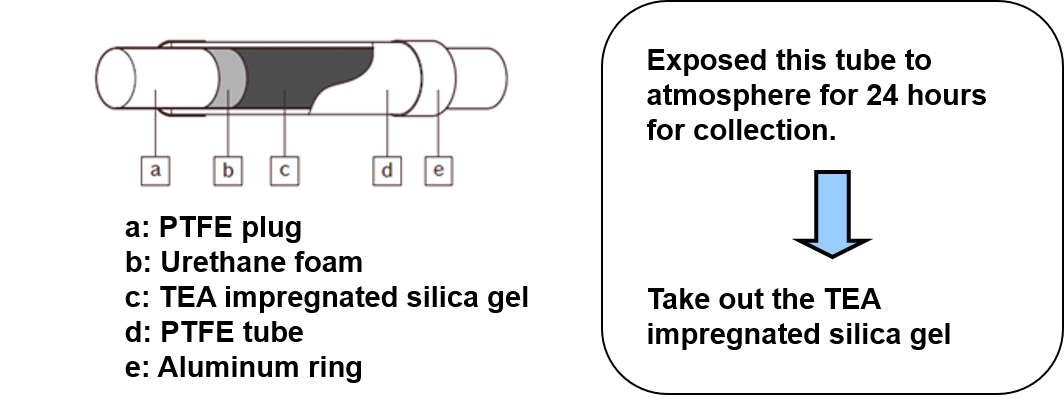
Figure 3. Usage of passive gas tube for collecting the sample in atmosphere
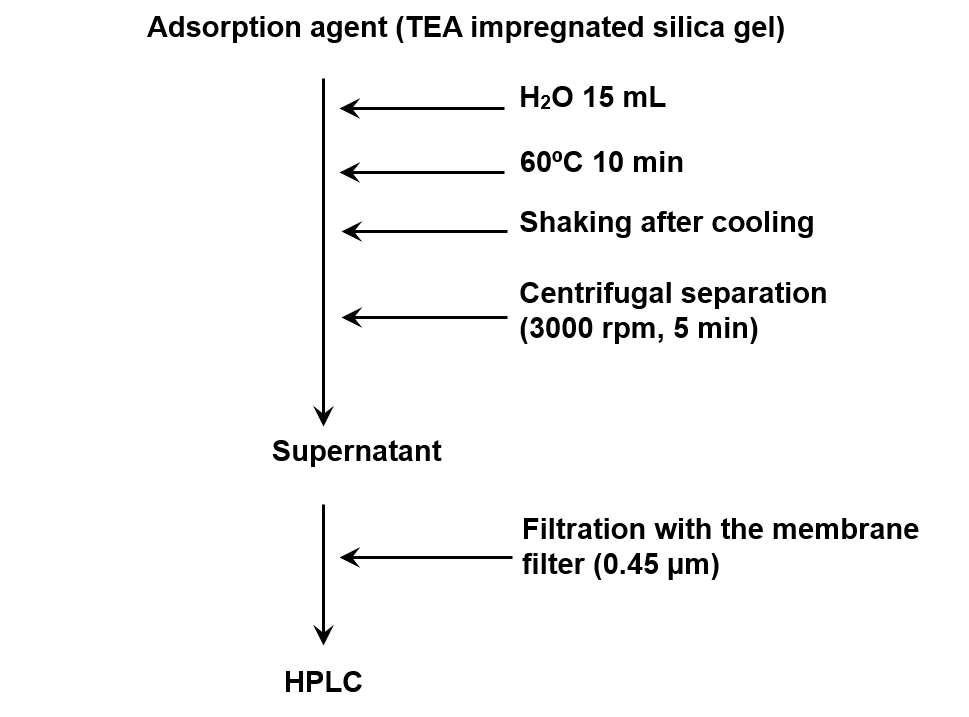
Figure 4. Extraction method from passive gas tube
Results
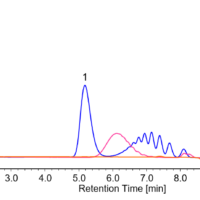
Figure 5 shows a chromatogram of the sample in the laboratory atmosphere collected with the passive gas tube. The calculated concentration of formaldehyde obtained was 0.0054 mg/L.
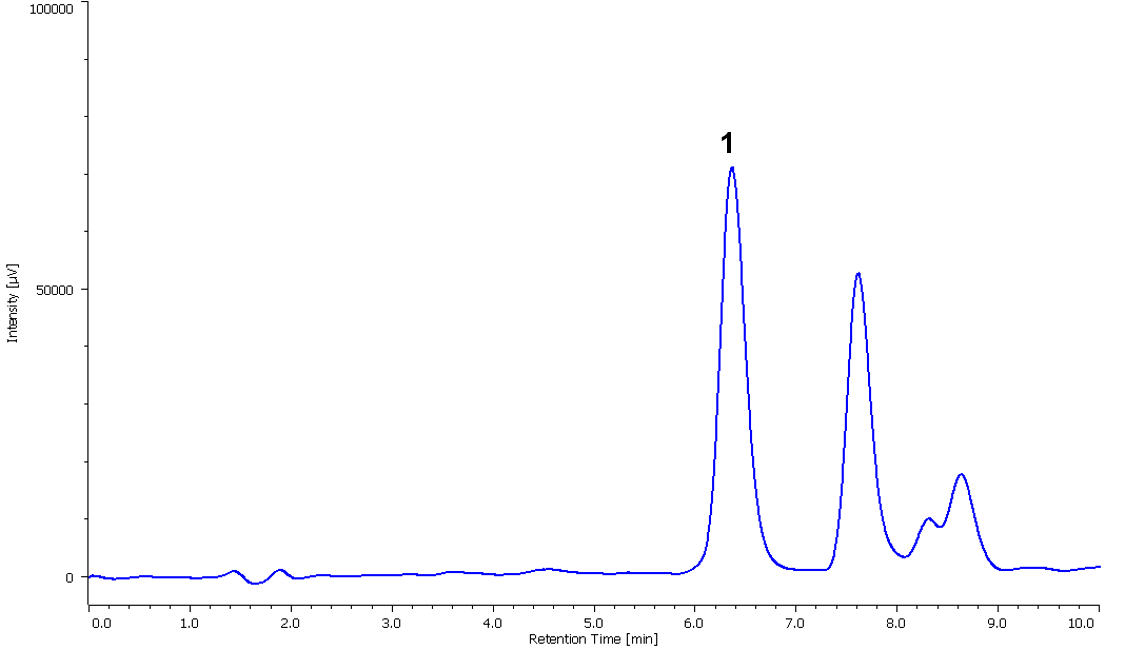
Figure 5. Chromatogram of sample in the laboratory atmosphere. (1: Formaldehyde (0.0054 mg/L))