Introduction
Among the food additives, there are several food preservatives. They have a function to inhibit proliferation of various microorganism which causes the rot of food, while many of them are toxic, and accordingly, the several countries/regions regulate the usage of such preservatives by the law. In Japan, these preservatives are regulated by Food Sanitation Act.
This article describes the analysis of three kinds of food preservatives, Benzoic Acid, Sorbic Acid and Dehydroacetic Acid, according to “Japanese Standards of Food Additives” which contains the relevant criteria and standards.

LC-4500 HPLC system
Experimental
Measurement conditions
Column: CrestPak C18S (4.6 mmI.D. x 150 mmL, 5 µm)
Eluent : 5 mmol/L Citrate buffer (pH 4.1) / Acetonitrile Methanol (70/20/10)
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Column temp.: 40 ºC
Wavelength: 230 nm
Injection volume: 10 µL
Standard sample: Benzoic acid, Sorbic acid, Dehydroacetic acid 2 µg/mL each in water
Figure 1 shows the structure of each preservative.
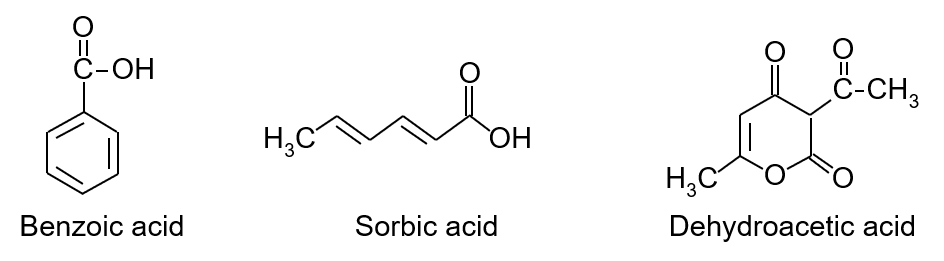
Figure 1. Structure of the preservatives
Keywords
Food additive, preservative, Benzoic acid, Sorbic acid, Dehydroacetic acid, C18 column, UV detection
Results
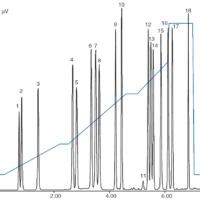
The chromatogram of standard mixture displayed in Figure 2 shows a good separation of the three components within 9 minutes.
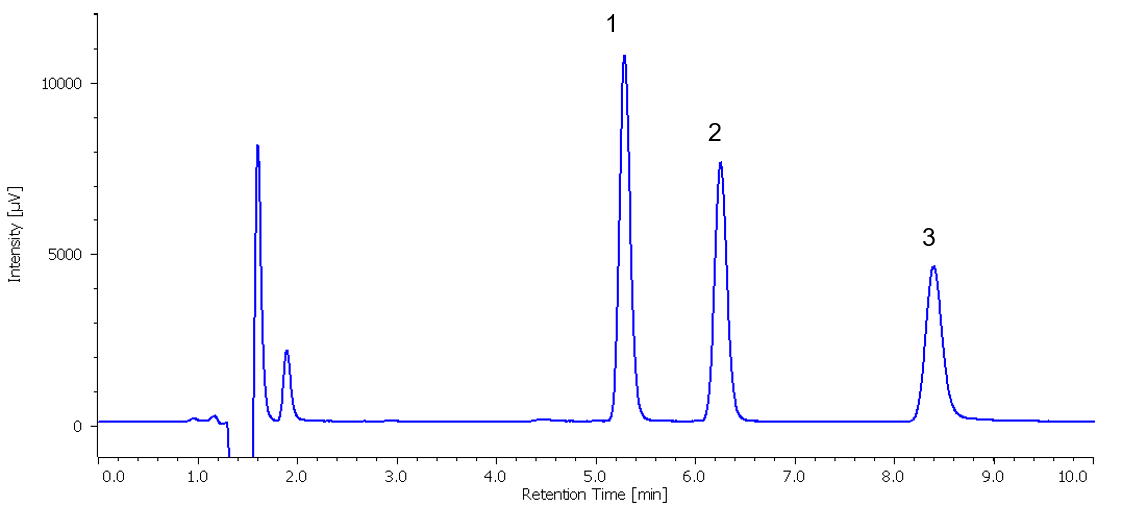
Figure 2. Chromatogram of standard mixture containing 3 preservative components (1: Benzoic acid, 2: Sorbic acid, 3: Dehydroacetic acid)

![Foreign material analysis by [Mixture Analysis] Foreign material analysis by [Mixture Analysis]](https://www.jasco-global.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/260MT0209_1-200x200.png)