Introduction
Heat-shielding glass has become popular as an eco-friendly material in the construction industry, it offers energy-saving and aids in reducing global warming. Several standards including ISO 9050 have been published with methods for determining the characteristic parameters of heat-shielding glass, including light transmittance/reflectance (for illuminant D65) and direct solar transmittance/reflectance/absorptance.
This application note demonstrates the evaluation of heat-shielding glass using methods that are compliant with ISO 9050 and JIS R 3106/3107, and the characteristic parameters were determined using a UV-visible/NIR spectrophotometer and an FTIR spectrometer.
Definitions of terminology
<Light transmittance, Light reflectance>
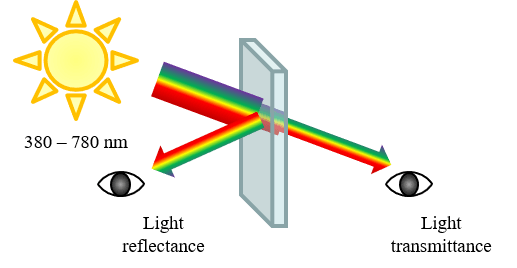 Definition: The brightness of light that is transmitted/reflected when sunlight is irradiated on a window
Definition: The brightness of light that is transmitted/reflected when sunlight is irradiated on a window
Standard: JIS R 3106:1998, ISO 9050:2003
<direct solar transmittance, direct solar reflectance, direct solar absorptance>
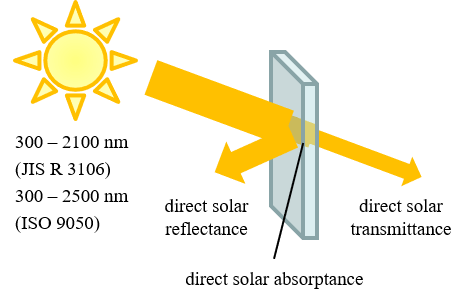 Definition: The amount of light that is transmitted/reflected/absorbed when sunlight is irradiated on a window
Definition: The amount of light that is transmitted/reflected/absorbed when sunlight is irradiated on a window
Standard: JIS R 3106:1998, ISO 9050:2003
<Thermal transmittance >
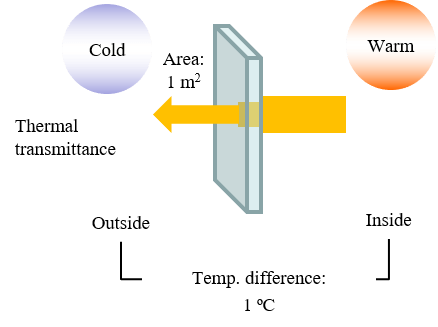 Definition: The amount of heat that is transferred through a 1 m2 window (for 1 hour) when the temperature difference between the inside and outside is 1 ºC. This also indicates the degree of heat transfer from a warm area to a cold area.
Definition: The amount of heat that is transferred through a 1 m2 window (for 1 hour) when the temperature difference between the inside and outside is 1 ºC. This also indicates the degree of heat transfer from a warm area to a cold area.
Standard: JIS R 3107:1998
*Reflectance spectrum by FTIR is required for calculating the thermal transmittance.
<Total solar energy transmittance>
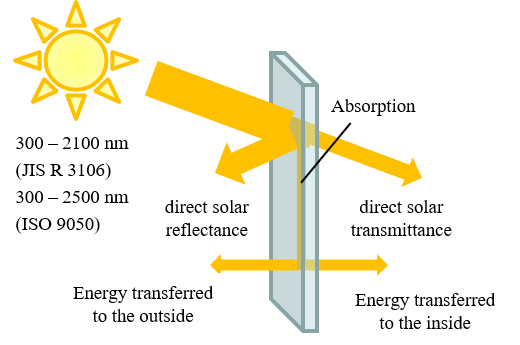 Definition: The amount of heat when sunlight enters a room through window. In other words, it also indicates the degree how easy the heat can be transmitted to the room.
Definition: The amount of heat when sunlight enters a room through window. In other words, it also indicates the degree how easy the heat can be transmitted to the room.
Standard: JIS R 3106:1998, ISO 9050:2003
*A reflectance spectrum measured by FTIR is required for calculating the total solar energy transmittance.
<UV-transmittance>
 Definition: The amount of light transmitted when UV light (UVA and UVB) from sun is irradiated on a window
Definition: The amount of light transmitted when UV light (UVA and UVB) from sun is irradiated on a window
Standard: ISO 9050:2003
<CIE damage factor>
 Definition: Value that represents what degree the color of a material is changed when sunlight is irradiated through window
Definition: Value that represents what degree the color of a material is changed when sunlight is irradiated through window
Standard: ISO 9050:2003
<Skin damage factor>
 Definition: Value that represents the degree to which skin is damaged when sunlight is irradiated on a window
Definition: Value that represents the degree to which skin is damaged when sunlight is irradiated on a window
Standard: ISO 9050:2003
<General color rendering index>
 Definition: An index that indicates the difference between the color of a material that is observed through window and the color when it is observed directly with sunlight irradiation.
Definition: An index that indicates the difference between the color of a material that is observed through window and the color when it is observed directly with sunlight irradiation.
Standard: ISO 9050:2003
Experimental
Evaluation system
V-770: UV-visible/NIR spectrophotometer
ISN-923: 60 mm dia. Integrating Sphere
FT/IR-4600: FTIR spectrometer
RF-81S: Infrared reflection attachment
VWST-964: Solar/visible light measurement and analysis program
Solar/visible light measurement and analysis program
Sample
Low-E Glass (Low Emissivity Glass)
Measurement conditions
<UV-visible/NIR spectrophotometer>
UV-visible band width: 5.0 nm
NIR band width: 20.0 nm
Scanning speed: 400 nm/min.
Response: 0.24 sec.
Data interval: 0.5 nm
<FTIR>
Resolution 4 cm-1
Accumulation: 64
Keywords
JIS R 3106, JIS R 3107, ISO 9050, Heat-shielding glass, direct solar transmittance/reflectance/absorptance, Light transmittance/reflectance for illuminant D65
Results
Figure 1 shows the results of measurements made using a UV-visible/NIR spectrophotometer and an FTIR spectrometer.
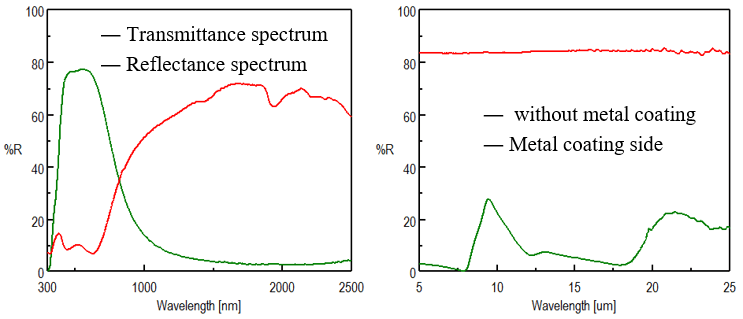
Figure 1. Measurement spectra by each analytical instrument (Left: UV-visible/NIR spectrophotometer, Right: FTIR spectrometer)
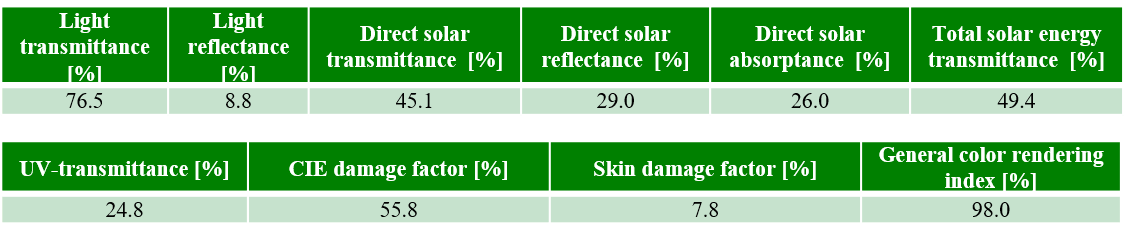
Table 1 and 2 shows the analysis results. The solar/visible light measurement and analysis program is used to quantify the performance of heat-shielding glass, and is recommended for product comparison and quality control. In addition, this program can also be used to evaluate a variety of products according to the following standards: JIS K 5602 (paint film), JIS K 5675 (paint), JIS A 5759 (Adhesive film), ISO 13837 (Road vehicles – safety glazing materials), ASTM E 903 (materials), ASTM E 424 (sheet materials) etc.
Table 1. Analysis results (JIS R 3106/3107)
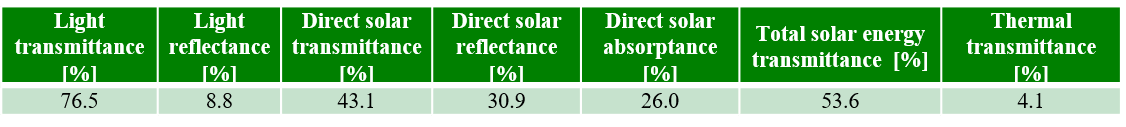
Table 2.Analysis results (ISO 9050)