Introduction
< Key Points >
Optical characteristics of prisms can be evaluated using absolute reflectance measurement system.
< Introduction >
Prisms are used in cameras, projectors, and telescopes to change the direction of light travel, combine light from different directions, and separate light into different wavelengths. The quality of prisms is generally evaluated in terms of their spectral characteristics at a given angle using an absolute reflectance measurement system (Fig. 1), which can set the angle of the incident light and the angle of the refracted light (the angle at which the incident light is detected when it emerges from the prism).

Fig. 1 Absolute reflectance measurement system
A cross dichroic prism (Fig. 2) is composed of right-angle isosceles prisms whose reflective surfaces are bonded together so that the prisms are orthogonal to each other.
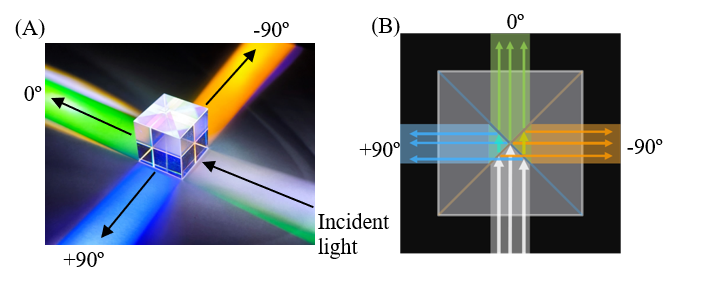
Fig. 2 A: Color decomposition by dichroic prism, B: Schematic view from above
It can decompose white light into three differently colored beams that emerge at different angles (color decomposition), or combine three orthogonal beams with different colors into a single beam (color synthesis), and is used in projectors and other optical devices.1) This report describes an evaluation of the characteristics of a cross dichroic prism using the JASCO absolute reflectance measurement system*.
- Since the properties of a prism depend on the film adhered to its surfaces, both the color-decomposition and color-synthesis properties can be evaluated in a single measurement.
Experimental
Sample
Cross dichroic prism
System
Instrument: V-750 UV-Visible spectrophotometer
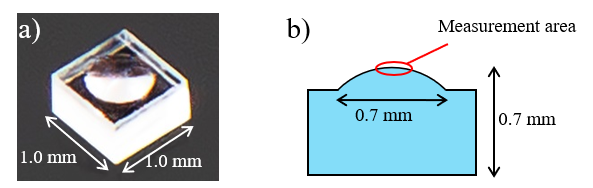
Accessory: ARMV-919 Automated absolute reflectance measurement unit, dedicated sample stage (Fig. 3)
Software: VWAM-968 Absolute reflectance measurement program
VWCD-960 Color evaluation (color diagnosis) program
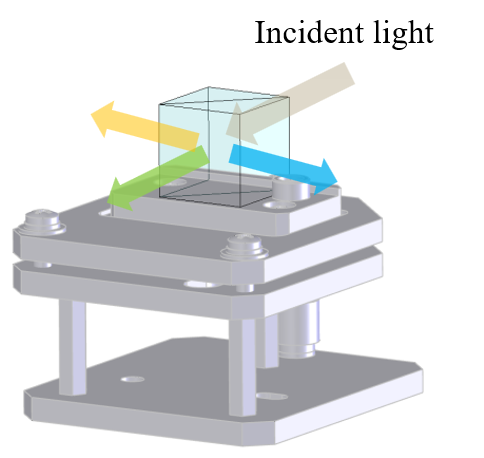
Fig. 3 Dedicated sample stage
Parameters
Configuration: Transmittance*1
Incidence angle: 0º
Detection angle: -90º, 0º (Fig. 4)*2
Polarizer: 45º (normal polarization)
Measurement range: 800 – 340 nm
Bandwidth: 5.0 nm
Scan speed: 400 nm/min
*1 The measurement at an angle of -90º is essentially a reflection measurement, but if a transmission arrangement is used, the 0º-and -90º measurements can automatically be performed in succession.
*2 By placing the sample upside down, the measurement results at -90º can be used as the results at +90º.
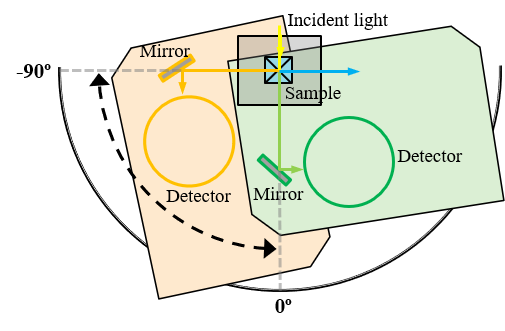
Fig. 4 Configuration of detector and mirror at -90º and 0º
Keywords
Prism, camera, projector, quality assessment, spectroscopic characteristics, spectrophotometer, absolute reflectance measurement system
Results
Figure 5(A) shows the measured transmission and reflection spectra for the cross dichroic prism. The spectra for the +90º and -90º directions represent the reflection characteristics of each reflective surface, while the spectrum for the 0º direction represents directly transmitted light. Therefore, the spectra exhibit a complementary relationship. Figure 5(B) presents the results of a color analysis of each spectrum. The color of light emerging from the prism in each direction is plotted on a chromaticity diagram based on the spectra.
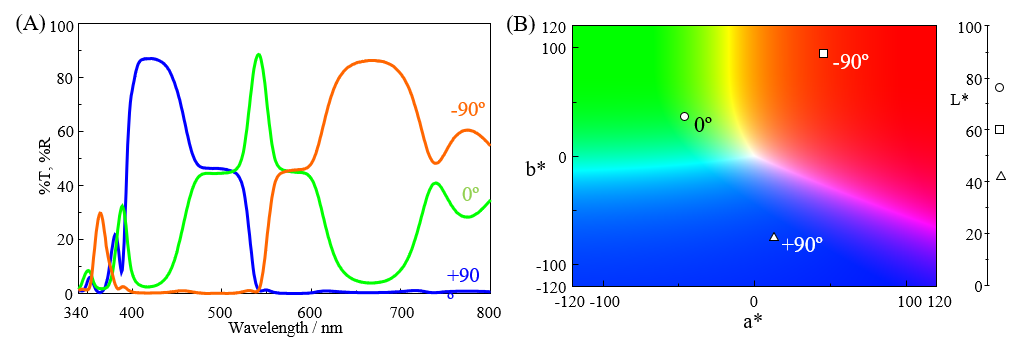
Fig. 5 A: Transmission and reflection spectra for +90º, 0º and -90º directions, B: Plot of calculated chromaticity values based on each spectrum
Conclusion
The spectral characteristics of a cross dichroic prism in three directions were evaluated using the JASCO absolute reflectance measurement system, which allows automatic measurement of light emerging at different angles from complex prisms and specially shaped prisms. Even for prisms that cannot be evaluated using conventional spectrophotometers, the optical properties can be objectively assessed using this system, making it useful for the characterization of optical elements and for quality control.
References
Kuninori Okuhara, ITE Technical Report, 32, 27, (2008). DOI: https://doi.org/10.11485/itetr.32.27.0_33