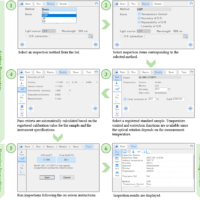
Introduction
< Key Point >
Instrument management functions support users in effectively maintaining data reliability.
Instrument management is crucial for accurate measurements using analytical instruments. Measurements should be performed after ensuring that the instrument is in good condition. P-4000 series polarimeters offer three management functions (daily check, validation, and self diagnosis) to help users carry out effective instrument management and ensure accurate measurements.
Table 1. Instrument management for P-4000 series polarimeters
| Function | What to inspect | Typical uses |
| Daily check | Light source energy, accuracy of optical rotation | Simple inspection at instrument start-up |
| Validation | Accuracy, repeatability, and linearity of optical rotation | Monthly comprehensive inspection |
| Self diagnosis | Hardware condition | Troubleshooting when measurement results are unusual |

Fig. 1. P-4000 series polarimeter
< Instrument Management >
Daily Check
Daily check is a simple instrument management function that inspects the light source energy and the accuracy of optical rotation. These inspections can be performed in just a few minutes, which is convenient for a daily instrument check at start-up. Inspection results are shown in a table in chronological order so that changes over time can be easily observed.
Table 2. Inspection items for daily check
| Item | Description |
| Light source energy | Inspects the intensity of the light source. A decrease in intensity due to deterioration of the light source leads to low accuracy and poor repeatability for optical rotation measurements. |
| Accuracy of optical rotation | Performs measurements using a calibrated quartz control plate and determines the deviation of the measured value from the calibrated value. |
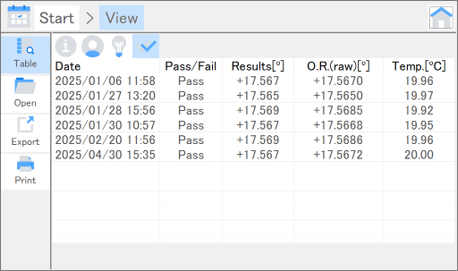
Fig. 2. Result table for accuracy of optical rotation
Validation
Validation inspects various instrument specifications, such as accuracy, repeatability, and linearity of optical rotation. When a particular pharmacopoeia is selected as the inspection method, inspections that are compliant with the selected pharmacopoeia are performed. When Basic is selected, the basic performance of the instrument is inspected. Validation takes two to fifteen minutes depending on the number of inspection items. Therefore, it is used to perform regular comprehensive start-up, weekly, monthly, or annual inspections.
| Inspection method | Inspection items | Remarks |
| Basic | Zero repeatability, and accuracy and repeatability of optical rotation | Basic performance of the instrument |
| U.S. pharmacopeia (USP) | Temperature control, and accuracy, repeatability, and linearity of optical rotation | Compliant with USP-NF 2024, Issue 3 |
| European pharmacopoeia (EP) | Accuracy and linearity of optical rotation | Compliant with EP11.0 (2022) |
| Japanese pharmacopoeia (JP) | Accuracy of optical rotation | Compliant with JP18 (2021) |
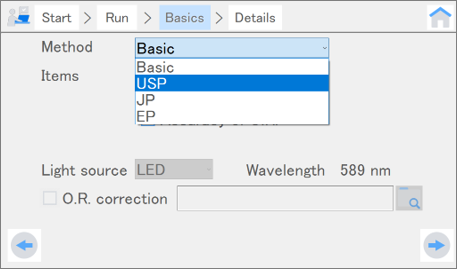
Fig. 3. Inspection methods for validation
Self Diagnosis
Self diagnosis automatically inspects the condition of hardware such as the light source, temperature sensors, and analyzer motor by a few simple taps on the touch screen. Performing a self diagnosis is recommended when the instrument does not pass the daily check or validation test, or unusual measurement results are obtained.
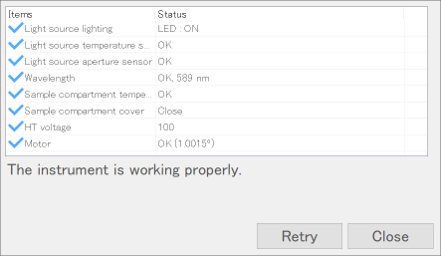
Fig. 4. Self-diagnosis results
Keywords
Polarimeter, instrument management, instrument maintenance, daily check, validation, U.S. pharmacopeia (USP), European pharmacopoeia (EP), Japanese pharmacopoeia (JP)
Conclusion
P-4000 series polarimeters provide three functions for instrument management. These functions support effective instrument inspections, which lead to more reliable data.
Refer to the application note 200-PL-0010 for details about each inspection item for validation.
References
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: June 7, 2021 The MHLW Ministerial Notification No. 220, “The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 18th edition”, (2021).
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention: “USP-NF 2024 Issue 3”, (2024).
- lCouncil of Europe: “European Pharmacopoeia 11th edition”, (2023).